How Xitadel Works Financially
— Xitadel
Xitadel offers Overcollateralized crypto bonds (LTT) with better fundraising without selling pressure for foundations. However, these financial products face a significant challenge. Unlike their traditional counterparts, they lack evaluations from established credit rating agencies. This void in conventional credit ratings introduced a need for new methods to assess creditworthiness and promote confidence. By compensating for this absence, advanced financial models are playing a pivotal role.
The Xitadel Financial Engineering Team has developed a sophisticated financial model that meticulously determines three critical parameters for LTTs. Liquidation ratio, Bond size, and Interest Rate. This comprehensive approach is designed to ensure a robust assessment of each parameter, which enhances both overall bond stability and investor appeal. The financial model is based on the most recent research paper, and over 1TB of traditional financial and crypto trading data are analyzed.

1. The Liquidation Ratio: The Core of Investor Protection
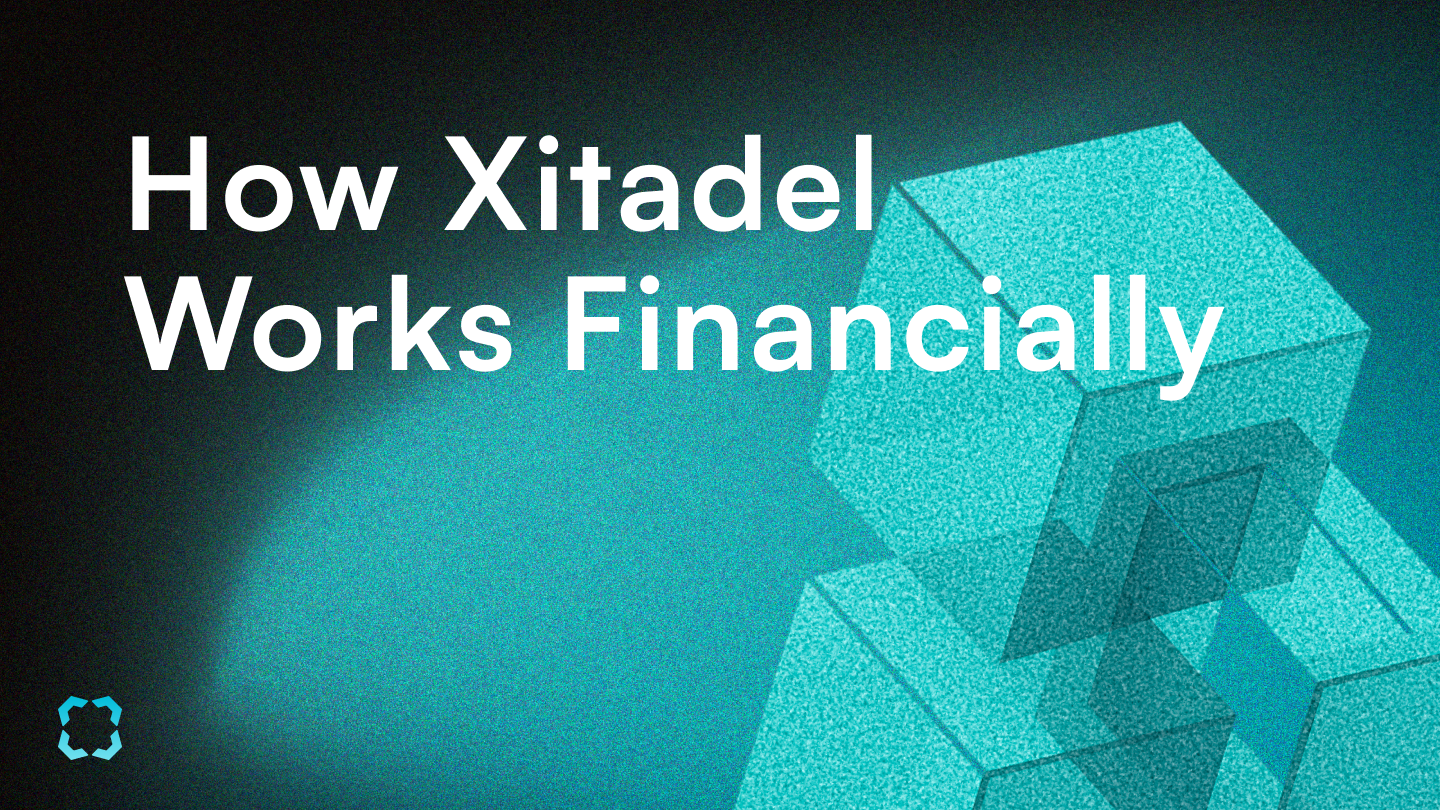
The liquidation ratio is a critical parameter that establishes the threshold of liquidation to cover potential losses. A well-calibrated ratio is essential for maintaining the bond's financial stability and investor confidence.
To determine an optimal liquidation ratio, the model employs a multi-faceted approach.
Market Impact: The model first assesses the potential impact of liquidating large collateral positions on market prices.
Kyle's Lambda, introduced by Albert Kyle, is mainly considered. This metric quantifies the price impact per unit of traded volume, providing insights into market liquidity and the potential cost of large trades. The formula is expressed as
ri,n=λi⋅Si,n+ϵi,t,
where ri,n is the percentage stock return, Si,n is the signed square-root dollar volume, λi is Kyle's Lambda, and ϵi,t is the error term.
Optimal Execution of Portfolio Transactions, which balances the urgency of liquidation with its associated costs to minimize the overall execution cost, is also considered for more sophisticated market impact forecast. The model also references Bloomberg's Transaction Cost Analysis (TCA) tools to offer empirical data on transaction costs. While crucial, this approach has limitations, as an excessive amount of collateral after liquidation could exacerbate the market and trigger a collapse, similar to the Luna incident.
Game Theory: To address the limitations of market impact analysis, Xitadel applies game theory to create a framework that ensures the repayment of principal and interest. This approach is designed to create a strategic dominance for a foundation to repay its debts. The model uses an equation to evaluate the decision to repay or default, incorporating variables such as the token leftover in the treasury, the price after default, the OTC discount after default, and the principal. Since a foundation holds a substantial amount of its governance tokens in its treasury, preventing a default is essential to preserving the value of these leftover tokens. Technically tokens in treasury are also softly committed as collateral.
Agent-Based Interactive Discrete Event Simulation (ABIDES): This framework is an agent-based market simulation that provides a high-fidelity virtual exchange for studying trading dynamics and risk. ABIDES can simulate thousands of trading agents interacting with a centralized exchange in real-time, incorporating realistic market microstructure features like network latencies and order messaging systems. It offers a controlled environment to evaluate how complex agent behaviors impact market outcomes, making it a powerful tool for risk estimation. Unlike traditional models that use static formulas or historical data, ABIDES organically generates market impact as an emergent result of supply-demand imbalances and strategic agent reactions.
2. Interest Rate: Attractiveness and Risk Compensation
The interest rate directly influences the bond's appeal to potential investors. A competitive rate compensates investors for the risks associated with the bond, including credit risk and market volatility. Setting the interest rate requires a careful assessment of market conditions.
The process of determining the interest rate begins with direct negotiations between the bond issuer and potential investors. Issuers, who provide collateral, aim to offer an attractive rate while minimizing their own borrowing costs. The quality and value of the collateral are a major factor in these discussions; higher-quality collateral can justify a lower interest rate due to reduced risk, whereas lower-quality collateral may require a higher rate to compensate for increased risk. Beyond these negotiations, the bond's interest rate is also benchmarked against broader market rates, such as government bond yields and central bank rates. This ensures that the bond remains competitive and appealing relative to other available investment opportunities.
3. LTT Size: The Balance Between Liquidity and Market Risk
The LTT size, or the principal amount of the bond, is a significant factor in its liquidity and marketability. While a larger bond issuance can attract investors seeking substantial investment opportunities, an excessively large size could increase the risk and lead to catastrophic outcomes during liquidation. Conversely, smaller bonds may lack appeal and traders of LTTs will suffer from lower liquidity.
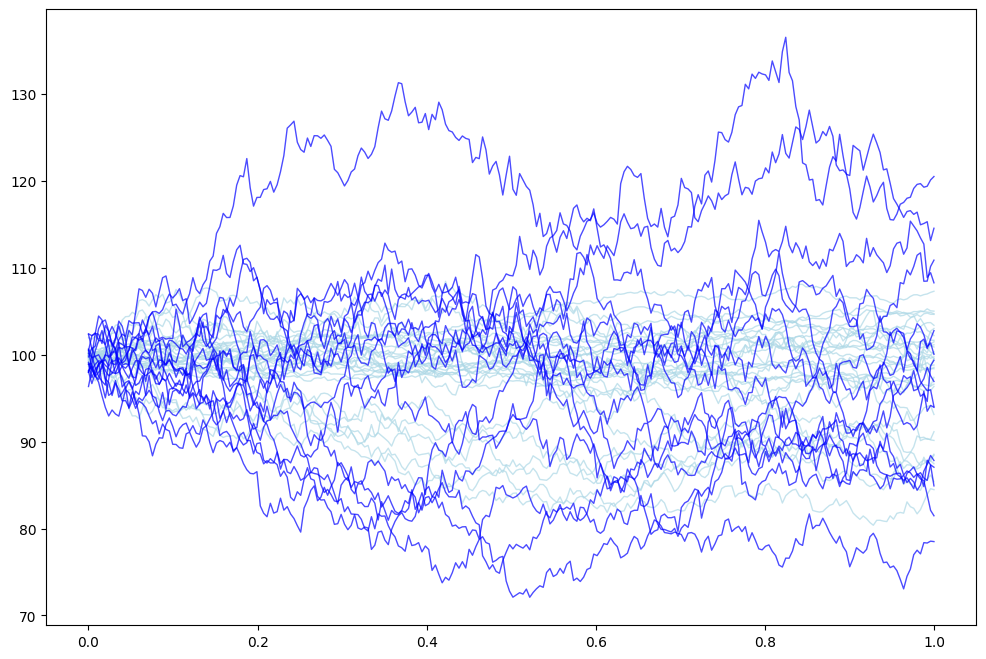
The model acknowledges that predicting black swan events is inherently impossible due to their extreme rarity and unpredictability. Therefore, to avoid disastrous events caused by market collapse from a large token drop, the bond size is conservatively limited. By using
Value at Risk (VaR) at 95% and 99% confidence levels, the model takes a conservative approach to determine an appropriate bond size for each token. This method helps to balance investor demand with the need to mitigate the risks associated with market impact.
Conclusion
The Xitadel Financial Engineering Team, our sophisticated financial model provides a robust framework for evaluating and structuring overcollateralized crypto bonds. By integrating complex methodologies like ABIDES, game theory, and VaR, our model creates a more secure and stable financial product. This innovative approach compensates for the absence of traditional credit ratings, while allowing for effective fundraising without the selling pressure foundations face.